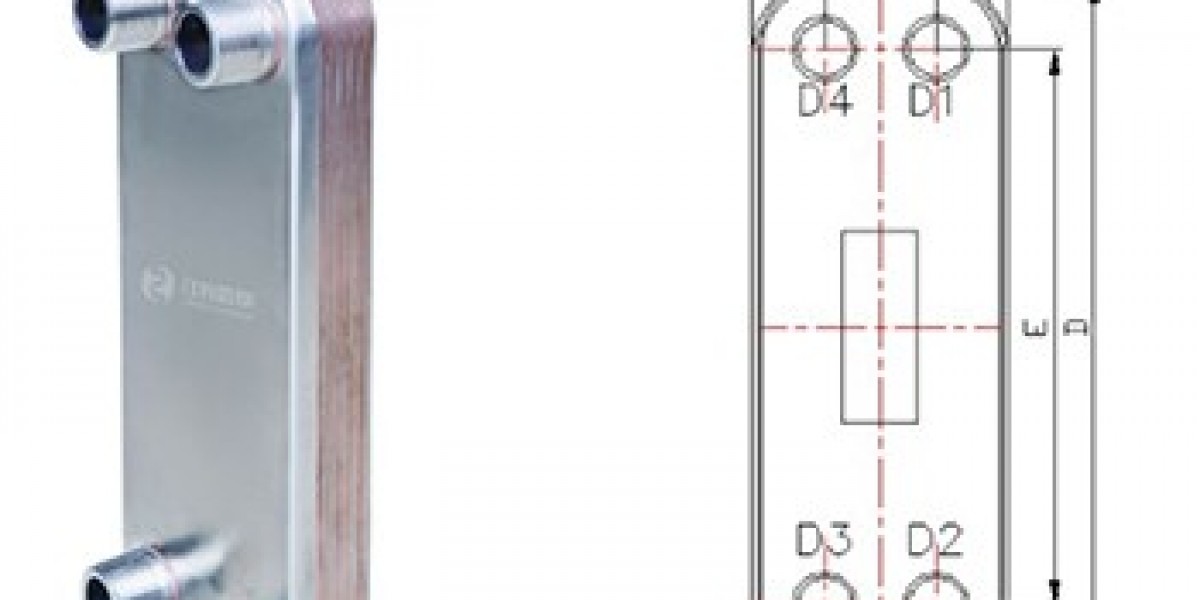
Brazed plate heat exchangers (BPHEs)have become increasingly popular in various industries due to their efficiency, compact design, and versatility. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of BPHEs, including their construction, applications, advantages, and maintenance practices.
What is a Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger?
Ahttps://www.yojointernational.com/Brazed-Plate-Heat-Exchanger/Brazed-Plate-Heat-Exchanger-ZL30.shtmlis a type of heat exchanger that utilizes thin, corrugated plates made from stainless steel. These plates are vacuum-brazed together using a filler material, typically copper or nickel. The design allows for efficient heat transfer between two fluids without mixing them.

Key Components ofBrazed Plate Heat ExchangerZL30
Plates: The primary elements that facilitate heat transfer.
Filler Material: Used to bond the plates together during the brazing process.
Cover Plates: Enclose the plate pack and maintain pressure.
Inlet and Outlet Ports: Allow fluids to enter and exit the exchanger.
Construction and Design
BPHEs are constructed as a package of corrugated plates arranged between front and rear cover plates. The corrugation enhances turbulence, which improves heat transfer efficiency.

Types of Materials
Stainless Steel (AISI 316): Commonly used for its corrosion resistance.
Copper: Often used as a filler material due to its excellent thermal conductivity.
Nickel-based Alloys: Suitable for applications involving ammonia or other corrosive fluids.
Advantages of Brazed Plate Heat ExchangersZL30
High Efficiency: BPHEs can achieve heat transfer coefficients up to six times greater than conventional heat exchangers due to their design.
Compact Size: Their small footprint makes them ideal for applications with limited space.
Low Hold-up Volume: This characteristic allows for rapid response times in temperature control applications.
Versatility: Suitable for various applications, including heating, cooling, and refrigeration.
Applications of Brazed Plate Heat ExchangersZL30
BPHEs are utilized across multiple sectors due to their adaptability:
HVAC Systems: Used in heating and cooling applications for buildings.
Industrial Processes: Employed in chemical processing, oil refining, and food production.
Refrigeration: Commonly found in chillers and condensers.
Renewable Energy: Used in solar heating systems and geothermal applications.

Operating Parameters
Understanding the operating parameters is crucial for optimal performance:
Maximum Operating Pressure: Typically ranges from 150 psig to 450 psig depending on the model.
Temperature Limits: Can operate at temperatures as high as 365F (185C) or as low as -320F (-196C).
Fluid Compatibility: Suitable for various fluids including water, oils, glycol mixtures, and refrigerants.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of a BPHE:
Mounting Position: Install vertically to allow for proper drainage of condensate.
Piping Connections: Ensure clean connections free from dirt and oils before installation.
Flow Arrangement: Typically configured in a counter-flow arrangement to maximize efficiency.
Safety Precautions
Always adhere to safety guidelines during installation to prevent leaks or injuries.
Use appropriate sealing materials compatible with the fluids being used.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance is vital for ensuring optimal performance:
Cleaning Procedures
Cleaning-in-Place (CIP): A method that allows for cleaning without disassembly.
Chemical Cleaning Agents: Use agents specifically designed for BPHEs to avoid damaging the plates.

Inspection
Regularly inspect connections and seals for leaks or wear. Ensure that all safety valves are operational.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Pressure Drop Problems: Often caused by fouling or blockages; regular cleaning can mitigate this issue.
Heat Transfer Inefficiencies: May indicate fouling or incorrect flow arrangements; check fluid velocities and flow rates.
Conclusion
Brazed plate heat exchangersare an excellent choice for various heating and cooling applications due to their efficiency, compact design, and versatility. Understanding their construction, applications, operating parameters, installation guidelines, and maintenance practices can help maximize their performance and lifespan.
Jiangsu Yuanzhuo Equipment Manufacturing CO., LTD.is also simply known as YOJO. Members of YOJO are the specialists who have gained rich experience in the heat transfer sector for many years and are holding the most advanced technology for the plate heat exchanger: research, design and manufacture.
Welcome to work with YOJO, we will provide the bestBrazed Plate Heat Exchangers ZL30solution for your specific needs.
E-mail:zy@jsyuanzhuo.com